POI 单元格类型CellType
1. 单元格类型
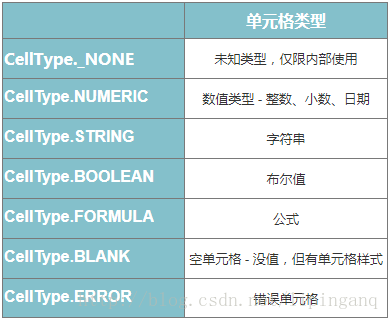
单元格的内容决定了单元格的类型,POI中定义的7种单元格类型:
- 日期数据对应的单元格类型是CellType.NUMERIC,默认以浮点型数显示,显示为日期格式需要设置单元格样式DataFormat
- 字符型单元格内容也可以为富文本RichTextString,可以对文本多部分设置字体Font
2. 错误单元格
Excel中存在错误单元格,在POI中是怎么表现的呢
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.FormulaErrorpackage org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.poi.util.Internal;
import java.util.HashMap;
/** * Enumerates error values in SpreadsheetML formula calculations. * * See also OOO's excelfileformat.pdf (2.5.6) */
public enum FormulaError {
@Internal
_NO_ERROR(-1, "(no error)"),
/** * Intended to indicate when two areas are required to intersect, but do not. * <p>Example: * In the case of SUM(B1 C1), the space between B1 and C1 is treated as the binary * intersection operator, when a comma was intended. end example] * </p> */
NULL(0x00, "#NULL!"),
/** * Intended to indicate when any number, including zero, is divided by zero. * Note: However, any error code divided by zero results in that error code. */
DIV0(0x07, "#DIV/0!"),
/** * Intended to indicate when an incompatible type argument is passed to a function, or * an incompatible type operand is used with an operator. * <p>Example: * In the case of a function argument, text was expected, but a number was provided * </p> */
VALUE(0x0F, "#VALUE!"),
/** * Intended to indicate when a cell reference is invalid. * <p>Example: * If a formula contains a reference to a cell, and then the row or column containing that cell is deleted, * a #REF! error results. If a worksheet does not support 20,001 columns, * OFFSET(A1,0,20000) will result in a #REF! error. * </p> */
REF(0x17, "#REF!"),
/** * Intended to indicate when what looks like a name is used, but no such name has been defined. * <p>Example: * XYZ/3, where XYZ is not a defined name. Total is & A10, * where neither Total nor is is a defined name. Presumably, "Total is " & A10 * was intended. SUM(A1C10), where the range A1:C10 was intended. * </p> */
NAME(0x1D, "#NAME?"),
/** * Intended to indicate when an argument to a function has a compatible type, but has a * value that is outside the domain over which that function is defined. (This is known as * a domain error.) * <p>Example: * Certain calls to ASIN, ATANH, FACT, and SQRT might result in domain errors. * </p> * Intended to indicate that the result of a function cannot be represented in a value of * the specified type, typically due to extreme magnitude. (This is known as a range * error.) * <p>Example: FACT(1000) might result in a range error. </p> */
NUM(0x24, "#NUM!"),
/** * Intended to indicate when a designated value is not available. * <p>Example: * Some functions, such as SUMX2MY2, perform a series of operations on corresponding * elements in two arrays. If those arrays do not have the same number of elements, then * for some elements in the longer array, there are no corresponding elements in the * shorter one; that is, one or more values in the shorter array are not available. * </p> * This error value can be produced by calling the function NA */
NA(0x2A, "#N/A"),
// These are POI-specific error codes
// It is desirable to make these (arbitrary) strings look clearly different from any other
// value expression that might appear in a formula. In addition these error strings should
// look unlike the standard Excel errors. Hence tilde ('~') was used.
/** * POI specific code to indicate that there is a circular reference * in the formula */
CIRCULAR_REF(0xFFFFFFC4, "~CIRCULAR~REF~"),
/** * POI specific code to indicate that the funcition required is * not implemented in POI */
FUNCTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED(0xFFFFFFE2, "~FUNCTION~NOT~IMPLEMENTED~");
private final byte type;
private final int longType;
private final String repr;
private FormulaError(int type, String repr) {
this.type = (byte)type;
this.longType = type;
this.repr = repr;
}
/** * @return numeric code of the error */
public byte getCode() {
return type;
}
/** * @return long (internal) numeric code of the error */
public int getLongCode() {
return longType;
}
/** * @return string representation of the error */
public String getString() {
return repr;
}
private static final Map<String, FormulaError> smap = new HashMap<String, FormulaError>();
private static final Map<Byte, FormulaError> bmap = new HashMap<Byte, FormulaError>();
private static final Map<Integer, FormulaError> imap = new HashMap<Integer, FormulaError>();
static{
for (FormulaError error : values()) {
bmap.put(error.getCode(), error);
imap.put(error.getLongCode(), error);
smap.put(error.getString(), error);
}
}
public static final boolean isValidCode(int errorCode) {
for (FormulaError error : values()) {
if (error.getCode() == errorCode) return true;
if (error.getLongCode() == errorCode) return true;
}
return false;
}
public static FormulaError forInt(byte type) throws IllegalArgumentException {
FormulaError err = bmap.get(type);
if(err == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown error type: " + type);
return err;
}
public static FormulaError forInt(int type) throws IllegalArgumentException {
FormulaError err = imap.get(type);
if(err == null) err = bmap.get((byte)type);
if(err == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown error type: " + type);
return err;
}
public static FormulaError forString(String code) throws IllegalArgumentException {
FormulaError err = smap.get(code);
if(err == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown error code: " + code);
return err;
}
}3. 实例
package hssf.sheet.cell;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellType;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
public class ExportDataCell {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xls");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.xls"));
exportExcel(out);
} finally {
out.close();
}
}
private static void exportExcel(BufferedOutputStream out) throws IOException {
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
//Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
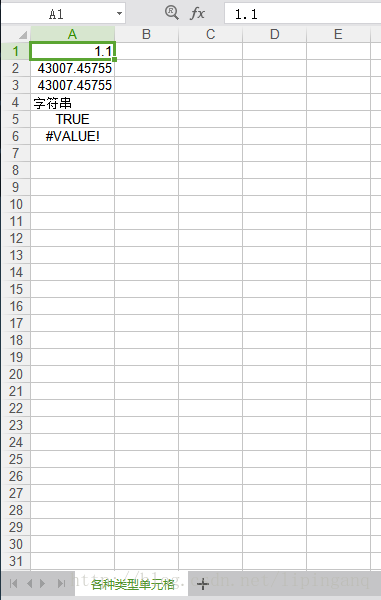
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("各种类型单元格");
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue(1.1);
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(new Date());
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(Calendar.getInstance());
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue("字符串");
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(true);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellType(CellType.ERROR);
wb.write(out);
}
}版权说明 : 本文为转载文章, 版权归原作者所有 版权申明
原文链接 : https://blog.csdn.net/lipinganq/article/details/78131857
内容来源于网络,如有侵权,请联系作者删除!
上一篇:POI 合并单元格